What is a Reverse Proxy and How Does It Work?
Picture a busy shop. You don’t walk straight into the storage room. You stop at the counter, give your order, and the clerk fetches what you need. That’s what a reverse proxy does online.
Instead of your browser hitting a server head-on, it speaks to the proxy. The proxy goes inside, talks to the server, and then brings the reply back.
This small step changes everything. Attackers can’t see the real server. Heavy traffic gets split across many machines. Pages load quicker because the proxy can hand out saved copies.
That’s the reverse proxy in plain words: a middle step that keeps servers safer, faster, and harder to break.
What is a reverse proxy?
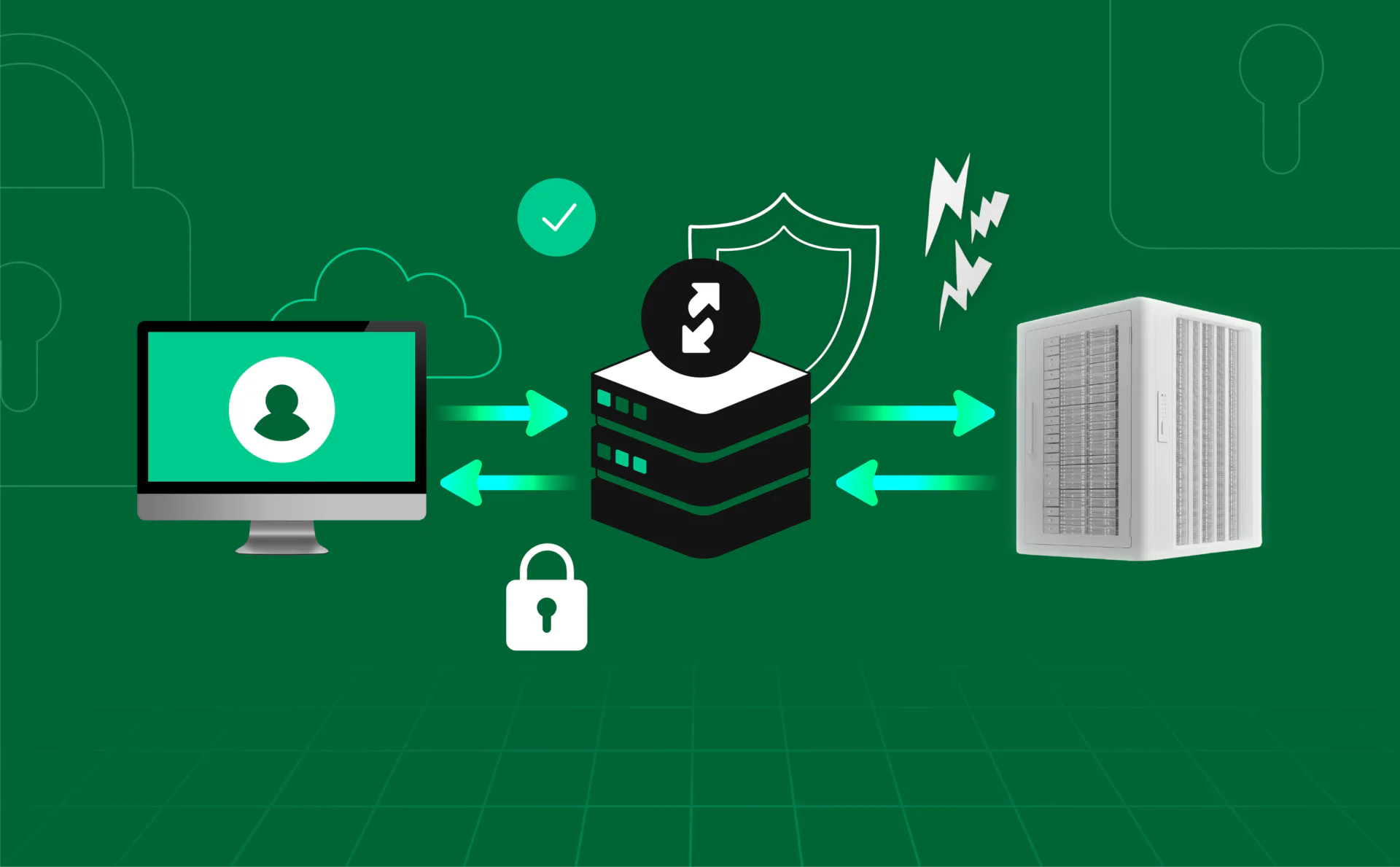
A reverse proxy is a server that stands in front of one or more web servers. Instead of your browser connecting to the server directly, the proxy receives your request first, then passes it on to the right server. It then sends the server’s reply back to you.
How it sits between users and web servers
Think of it as a middle layer. On one side are the users visiting a website. On the other side are the servers that store the site’s data. The reverse proxy sits between them, taking all incoming traffic, deciding where it should go, and sending back the right response.
Why it called “Reverse” compared to a Forward proxy
A forward proxy sits in front of users and hides their identity from websites. A reverse proxy does the opposite. It sits in front of servers and hides the servers from users. That’s why it’s called “reverse” — because the direction of protection is flipped.
Reverse proxy vs forward proxy
A forward proxy sits in front of users. When you browse the web through a forward proxy, the websites you visit never see your real IP address. They only see the proxy. This protects your identity, helps you bypass restrictions, and lets you control what users can or cannot access.
A reverse proxy does the opposite. It sits in front of servers. When you visit a website that uses a reverse proxy, you never connect to the real server directly. You only see the proxy. This keeps the server hidden, shields it from attacks, and makes it easier to manage large amounts of traffic.
How does aReverse proxy work?
A reverse proxy sits between you and the server. When you visit a website, your request goes to the proxy first. The proxy then decides which server should handle it, collects the reply, and sends it back to you. You never talk to the real server directly — the proxy is always the middleman.
- You send a request → it reaches the proxy.
- Proxy forwards it to the right server.
- Server responds → proxy sends the result back.
- Extra tasks: block bad traffic, cache content, balance heavy loads
Benefits of using a Reverse proxy
A reverse proxy is more than a middleman. It adds real value by protecting servers, spreading traffic, and speeding up websites. Here are the key benefits you get:
- Load balancing – split traffic across servers so no single machine crashes under pressure.
- Protection from attacks – keep the real server’s IP hidden, making targeted attacks harder.
- Global server load balancing (GSLB) – send users to the closest server for faster response times.
- Caching – save and serve repeat content quickly instead of hitting the server each time.
- SSL encryption – handle the heavy work of encrypting and decrypting connections.
- Monitoring and logging – track requests and behavior to spot issues or threats early.
Common reverse proxy use cases
A reverse proxy is useful anywhere a website or application needs to stay secure, fast, and reliable. It works as a control point for traffic and can be set up to handle different jobs depending on the needs of the business.
- Handle high traffic – spread requests across multiple servers to keep sites online.
- Defend against attacks – hide the real server’s IP and block harmful traffic like DDoS.
- Speed up sites with caching – serve stored copies of content for faster load times.
- Provide secure access – act as a gateway for staff or partners to reach internal apps safely.
- Filter traffic – block bots, spam, or restricted content before it reaches the server.
- Compress data – shrink files before sending them to users for quicker delivery.
- Centralize authentication – check user logins before letting requests reach backend servers.
- Host multiple sites – one proxy can manage traffic for several domains at once.
- Failover support – if one server goes down, send traffic to another automatically.
- Route by rules – direct certain requests to specific servers (by region, URL, or device).
FAQ
What is the main purpose of a reverse proxy?
To protect servers and manage traffic. It hides the real server, spreads requests across machines, and delivers content faster.
How is a reverse proxy different from a forward proxy?
A forward proxy hides users from websites. A reverse proxy hides servers from users. The direction of protection is reversed.
Is a reverse proxy the same as a load balancer?
Not exactly. A load balancer only distributes traffic, while a reverse proxy can also cache content, block attacks, handle SSL, and monitor traffic.
Do all websites need a reverse proxy?
No, but any site with high traffic, security risks, or performance needs will benefit from one. Small personal sites may not need it, but businesses almost always do.
Can a reverse proxy stop DDoS attacks?
Yes. Since users only see the proxy, attackers can’t target the real server directly. The proxy can filter or absorb harmful traffic before it reaches the server.
Conclusion
A reverse proxy is a simple idea with powerful results. It sits in front of servers, handles every request, and decides how to respond. By doing this, it keeps the real server hidden, blocks attacks, balances heavy traffic, and speeds up delivery. That’s why most modern websites rely on reverse proxies — they make the internet safer, faster, and more reliable for everyone.